RDA Value – Relative Dentin Abrasion
What role does toothpaste play in enamel abrasion?
Toothpaste has many functions. Besides freshening breath and preventing tooth decay, it should above all, clean teeth thoroughly! To achieve this, toothpastes contain small particles that help remove plaque, food residue and bacteria.
In the process, the cleaning particles in the toothpaste – especially in the case of aggressive whitening toothpastes – can also remove a minimal amount of the tooth enamel. This process is called abrasion. The abrasiveness of a toothpaste is indicated by its RDA value. This stands for the so-called Relative Dentin Abrasion.
This article explains what you need to know about the RDA value and which values are good for which application purpose. In addition, recommendations concerning which RDA value is specifically relevant for children and why the Kinder Karex Toothpaste cleans thoroughly while being gentle on a child’s teeth will be given.
What is the RDA value?
RDA is the short form for radioactive or relative dentin abrasion. To be precise, this complicated sounding term tells us how much a tooth “abrades” dentin (i.e. the interior of teeth) under laboratory conditions. In other words, it refers to the abrasion of the tooth substance caused by a toothpaste. In a figurative sense, the brushing performance of a toothpaste can also be indirectly derived from this.
How is the RDA value measured?
In a laboratory, the cleaning performance of a toothpaste is tested under standardized conditions in comparison to a reference value. Therefore, the R often stands for relative dentin abrasion. At the same time, or alternatively, the term radioactive dentin abrasion is also commonly used, as the tooth structure is irradiated for the measurement. This examination takes place in vitro, i.e. not on living organisms.
Significance of the RDA value
Although the RDA value is probably the best-known unit of measurement for the abrasion of a toothpaste, it is not to be viewed entirely uncritically and is also not to be found on every toothpaste. There is no requirement to declare the RDA value. The declaration is voluntary and is handled differently by different manufacturers.
However, the major criticism of the RDA value and alternative methods, such as the PCR value (Pellicle Cleaning Ratio) or REA (Radioactive Enamel Abrasion) is that the results from the laboratory cannot be directly transferred to daily use. Many other effects, such as the type of toothbrush or the pressure applied when brushing, also have an influence on abrasion1. Furthermore, the RDA value is measured on dentin, which is not directly transferable to abrasion on enamel.
RDA value table
The higher the RDA value, the higher the abrasiveness of the toothpaste and thus the dentin abrasion. The RDA scale can be roughly divided into four levels:
- Below 30: Very low abrasiveness with low cleaning power
- suitable for toothpastes for babies
- 30 to 50: Low abrasiveness with a good ratio between abrasion and cleaning effect
- suitable for daily dental care of baby teeth
- 50 to 80: Medium abrasiveness with a good ratio of abrasion to cleaning efficiency
- suitable for daily use for adults
- Over 100: Very abrasive, e.g. in toothpaste for white teeth
- not at all suitable for permanent use
Which RDA value is a good one?
In general, the value for a toothpaste for daily use in adults, should be between 30 and 80. For values below 30, the cleaning effect might be too weak for healthy teeth and plaque can hardly be sufficiently removed. For values above 80, the toothpaste is highly abrasive and might damage tooth enamel (or dentin) if used too frequently.
However, the RDA value alone does not necessarily determine whether tooth structure will be harmed or not. Which RDA value is actually good for you or your children also depends on a number of individual factors:
- Toothbrush: Depending on whether you use a toothbrush with soft or hard bristles, you should choose a toothpaste with an appropriate RDA value. A toothbrush with hard bristles also contributes to increased abrasion. Particularly with toothbrushes for children care should be taken to choose a soft one. Where electric toothbrushes are used, a toothpaste with a low to medium RDA value is usually sufficient.
- Tooth brushing technique: How the teeth are brushed can also influence whether additional enamel is removed. The teeth should be gently brushed, and horizontal movements should be avoided in order to protect the teeth and gums. Parents should pay attention and ensure their children use the correct tooth brushing technique.
- Condition of the teeth: Teeth with dentin hypersensitivity or exposed necks of teeth can be a sign that the enamel is already damaged. In this case, it is recommended that you use toothpastes with a lower dentin abrasion. Patients who grind their teeth (bruxism) also suffer damage to the tooth substance and should be particularly gentle when cleaning their teeth.
- Baby teeth: Baby teeth enamel is only half as thick as that of permanent teeth. Therefore, tooth for babies and toddlers should also have a rather low RDA value.
- Desired result: To remove tooth discolouration, special whitening toothpaste is often used to whiten teeth. These are often characterized by a particularly high abrasion value. For this reason, such toothpastes should only be used in consultation with your dentist and never on a long-term basis.
Which RDA value is recommended for children?
As the enamel of baby teeth is not so strong, a value between 35 and 50 is recommended for children’s toothpaste. This achieves a good compromise between good cleaning performance and simultaneous protection of the tooth structure.
However, a survey conducted by the opinion research institute forsa, on behalf of the KKH health insurance fund, showed that just under half of children between the ages of 3 and 12 brush their teeth with an adult toothpaste. Since the RDA value of adult toothpaste is often higher than the recommended abrasion value for baby teeth, this can lead to damage to tooth enamel (or dentin), if used every day.
Furthermore, the fluoride content in toothpastes for adults is higher than that in children’s toothpastes. While a fluoridated toothpaste for children may contain a maximum of 1,000 ppm fluoride, a fluoride content of 1,500 ppm is permissible in toothpastes for adults. In children, an increased intake of fluoride can lead to so-called dental fluorosis. Fluorosis can be seen when white or brown spots are visible on permanent teeth.
Kinder Karex RDA value
Toothpastes especially for babies, children and adolescents can also have an RDA value above 50, depending on the manufacturer. As a result, even baby teeth with their thin enamel, can be damaged by brushing with such toothpastes.
If intensive brushing by children and then by their parents, is added to this, it has consequences for the baby teeth. The enamel becomes thinner and thinner, making it more susceptible to decay and pain. The gums can also be damaged.
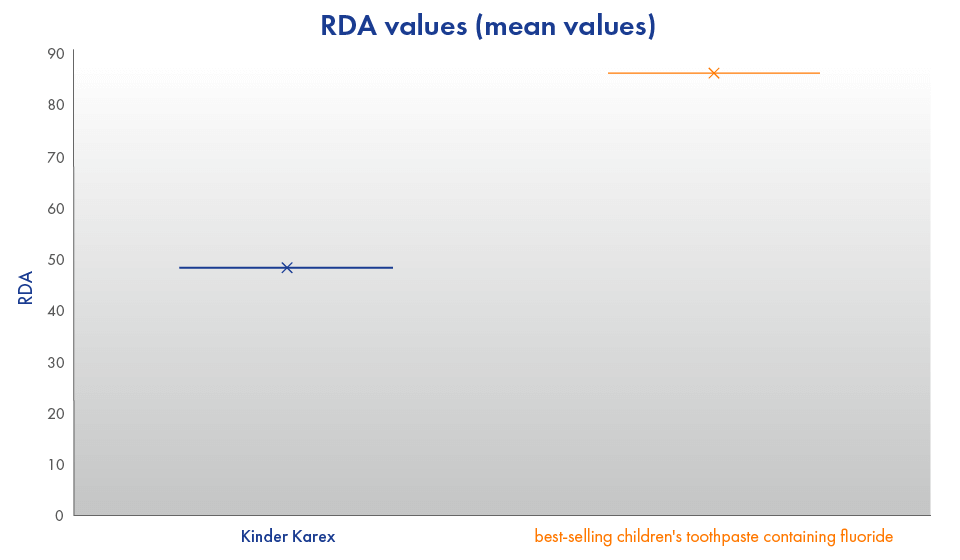
The figure shows the result of the measured average RDA values of Kinder Karex toothpaste and that of a commonly purchased fluoride-containing children’s toothpaste. The RDA value of Kinder Karex Toothpaste is below 50, which is in a good cleaning and less abrasive range. This allows a thorough removal of plaque without damaging the delicate enamel of baby teeth.
Sources:
- Enax, J; Epple, M.: The characterization of cleaning agents in toothpastes; Deutsche Zahnärztliche Zeitschrift (German Dentist Magazine); 2018; 73 (2), p.100ff






![[Translate to en_DE:] Zahnpasta Inhaltstoffe [Translate to en_DE:] Zahnpasta Inhaltstoffe](/fileadmin/_processed_/6/3/csm_karex-menu-zahnpasta-inhaltsstoffe_f2adc4e78d.jpg)