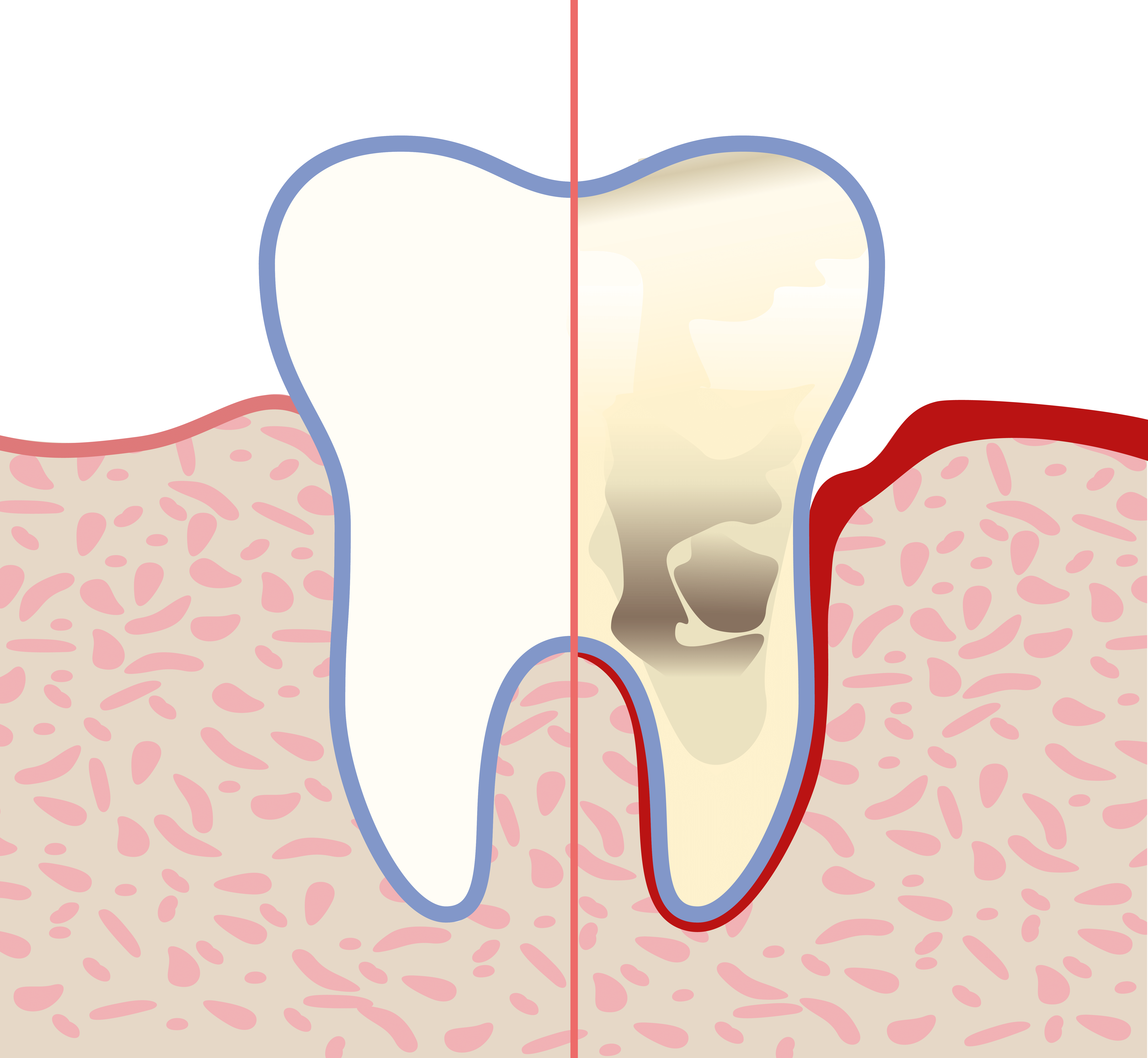
Inflammation of the gums – gingivitis and periodontitis
Inflamed gums are often red and swollen and may even bleed when the teeth are cleaned. More than 50% of adults (DMS V, 2016) in Germany suffer from gum inflammation. And gum inflammation is the most common cause of tooth loss in adults (DMS V, 2016).
In most cases, the superficial inflammation of the gums (the medical term for this is gingivitis) is due to poor oral hygiene. As such, the bacteria which attack the gums can increase rapidly. If the inflammation goes untreated, it can spread to the jaw and gum pockets can form leading to periodontitis. Periodontitis is irreversible and can lead to tooth loss.
Read more about the symptoms, causes, treatment and prevention of gum inflammation.
Symptoms of gum inflammation
Gingivitis and periodontitis are only rarely painful. There are other typical signs of gum inflammation.
Signs of gingivitis:
- Bleeding from the gums (especially when brushing the teeth and during interdental care)
- Sensitive, red and swollen gums
- Gum recession
- Exposed tooth necks and resulting pain-sensitive teeth
- Bad breath
- The red areas may even feel warm or hot
Symptoms of periodontitis:
As with simple gum disease, periodontitis is associated with gum bleeding, redness and swelling of the gums, gum recession and bad breath (halitosis). Further symptoms can also be observed:
- A bad taste in the mouth caused by pus from the gum pockets.
- Loosening of teeth or partial dentures
- Sharp or dull pain in the jaw when chewing
Gum disease often goes unnoticed by those affected because the initial symptoms are only mild or are not recognised as warning signs
Determining gum inflammation
In order to detect and treat gum inflammation as early as possible, you should regularly examine your teeth and gums yourself for the first signs.
Check your toothbrush. If the bristles are coloured red, your gums may be bleeding due to the light pressure applied by the toothbrush. This can indicate the start of an infection.
Check the colour of your gums. Healthy gums are light and pink. If you notice colour changes and your gums look dark and red in some places, this is a sign of inflammation.
How do your gums feel? In the initial stages of gum inflammation, the gums may be soft and swollen. Healthy gums on the other hand are firm and do not retract from the teeth.
Causes of inflamed gums
Gum inflammation is triggered by a "dysbiotic biofilm". A biofilm consists of different microorganisms and bacteria that occur completely naturally in our oral cavity. Insufficient cleaning of the teeth and external factors (e.g., smoking) mean that the balance between the biofilm and gums is no longer maintained and plaque can form.
Some microorganisms produce toxins which penetrate the gums and encourage inflammation. The gums swell up, become red and may feel warm. Failure to pay attention to gingivitis (early stage) can be associated with much more serious symptoms.
If left untreated, in many cases gingivitis can progress into periodontitis. This refers to inflammation of the entire periodontium, where degradation of the jawbone can also not be ruled out.
Various factors can lead to gum inflammation. Even when the teeth are brushed daily, the following aspects can cause inflammation:
- Prescription and over-the-counter medicines (antidepressants and cold remedies) lead to dry mouth as a side effect. Sufficient saliva production is important, however, as it helps to keep teeth clean by controlling the growth of bacteria. That's why: The less saliva you produce, the greater the risk of gum inflammation.
- Prescription and over-the-counter medicines (antidepressants and cold remedies) lead to dry mouth as a side effect. Sufficient saliva production is important, however, as it helps to keep teeth clean by controlling the growth of bacteria. That's why: The less saliva you produce, the greater the risk of gum inflammation.
- Viral and fungal infections (e.g., herpes and mouth ulcers).
- A very low calcium diet without vitamins B and C increases the risk of gum inflammation.
- Diseases such as diabetes, cancer, HIV and AIDS result in an increased risk of gum inflammation.
- Smoking increases the likelihood of gum inflammation.
- Hormonal changes due to pregnancy can result in gum problems in 60-70% of pregnant women (pregnancy gingivitis).
- Overly zealous tooth brushing, which injures the gums or gradually brushes them down, is also a risk factor for inflammation.
Research results have shown that around 30 per cent of all people are naturally more disposed to gum inflammation regardless of other health factors.
Gum inflammations can have far-reaching consequences. Not only tooth loss, but also an impairment of the cardiovascular system has been proven in studies.
Preventing gum inflammation
Regular trips your dentist - twice a year - allow gum disease to be detected and treated early on. Provided neither the periodontium nor the bones and connective tissue are affected, the gum inflammation can be repaired.
Professional tooth cleaning aids oral hygiene at home. Depending on your risk, you should have your teeth cleaned professionally one to two times a year. Some health insurance providers cover the costs of this.
Good oral hygiene and thorough teeth cleaning, which you do yourself every day, are the best ways to prevent gum inflammation, such as gingivitis and periodontitis:
- Clean your teeth twice a day to remove plaque from the teeth and gums.
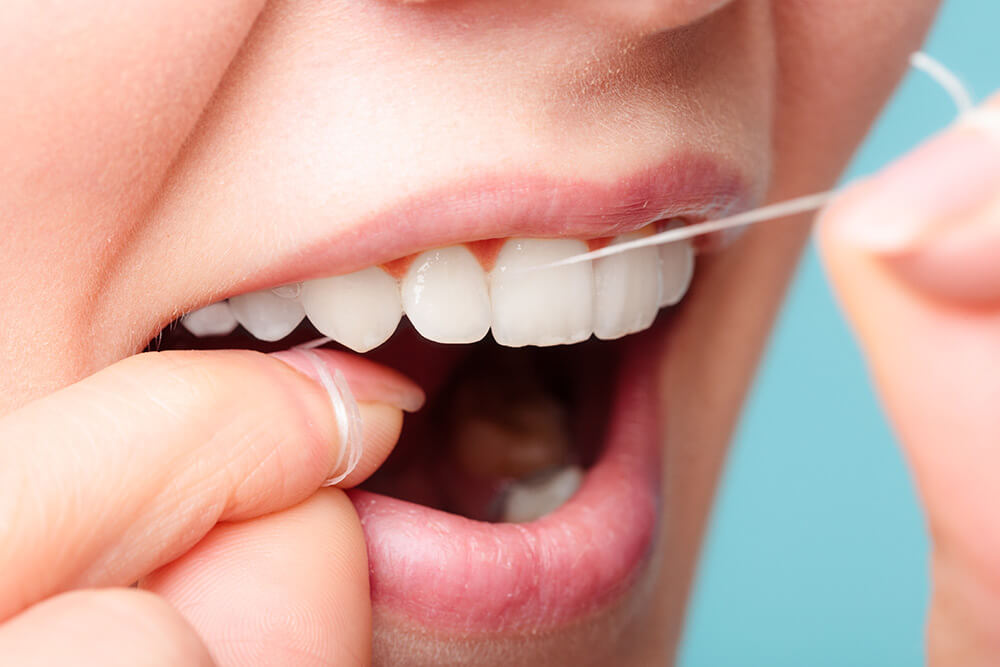
- Use floss. This loosens and removes food residues between the teeth and plaque below the gumline.
- A mouthwash also helps to rinse away loosened plaque and reduce the bacteria that cause gum inflammations.
- A gel like Karex Tooth Protection Gel prevents the accumulation of bacteria that cause inflammation of the gums and thus prevents gum problems.
This may also be of interest to you:

Caries: How to protect your teeth
Karies ist weltweit eine der häufigsten Krankheiten. Erfahren Sie hier mehr über Karies und die Ursachen.

Sensitive teeth – when enjoying food becomes impossible
Sensitive teeth are often caused by exposed tooth necks or defects in the dental enamel, find out more about this.

Help for dry mouths
Dryness of the mouth has many causes and can have serious consequences for tooth health. Find out more here.